New anti-bullying trial ‘significantly reduced incidents of bullying’
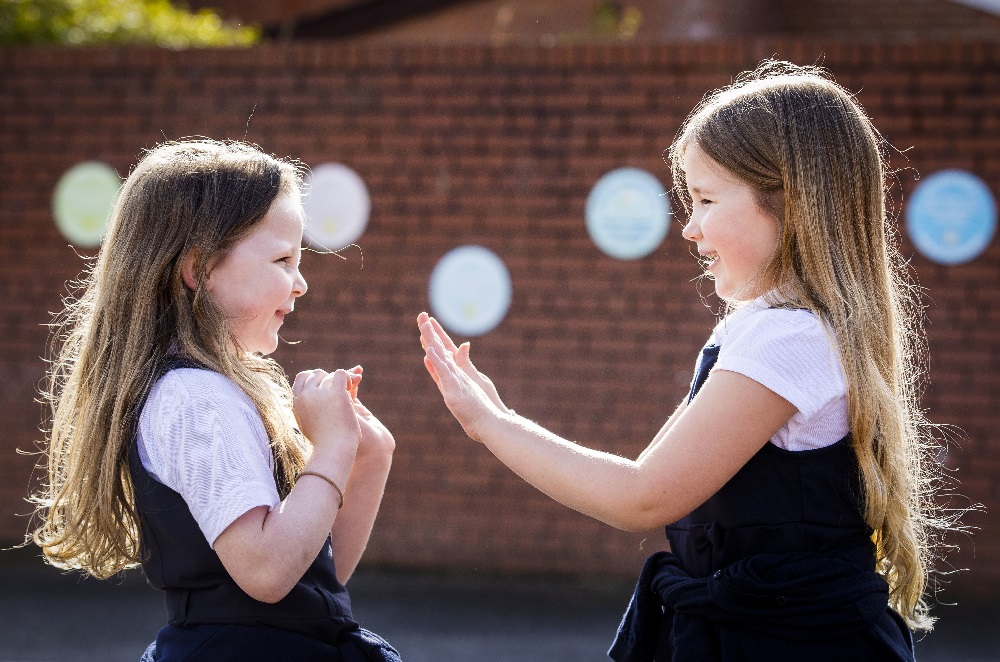

The largest trial of its kind in the UK has shown how a low-cost, structured, anti-bullying programme can improve social dynamics in primary schools and reduce victimisation.
The year-long trial of the KiVa school based bullying prevention programme was implemented in over 100 primary schools across Wales and England and involved over 11,000 students.
The programme significantly reduced incidents of bullying and was equally effective across socio-economically diverse schools and from small rural schools to large, urban ones. The study was funded by the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR).
Empathetic
The ‘KiVa’ programme focuses on the behaviour of all children and emphasises the role that bystanders can play. Children in schools that implemented the programme were 13% less likely to report being bullied, compared to schools using standard procedures.
The schools undertaking KiVa also reported that their children were more empathetic towards victims and that children’s problems with their peers were reduced. Considering budget restrictions in schools across Wales, health economists from Bangor University found that KiVa is a good, low-cost intervention.
Professor Judy Hutchings, from the Centre for Evidence Based Early Intervention at Bangor University, said: “Bullying in childhood is one of the biggest risk factors for later mental health problems in childhood, adolescence and beyond.
“Unfortunately, it is widespread in UK schools; and while all schools are required to have a bullying policy, it’s rarely evidence-based. The KiVa ‘whole school’ approach has had really significant effects on bullying in other countries because it focuses on everyone’s behaviour, and removes the social rewards usually gained by the perpetrators.”
The Programme
The Finnish Kiusaamista Vastaan (“Against Bullying”), or KiVa, programme, is based on research that demonstrates that bystanders – children who are present, but not directly involved in bullying incidents – have a major role to play in defending the victim, making bullying less socially acceptable, and so reducing the motivation of bullies.
The research is the largest randomised controlled trial to date of the KiVa programme outside Finland, involving 118 schools across Wales and England.
Half the schools adopted Kiva and half continued standard practice, and data was obtained from 11,111 pupils who filled in surveys about bullying, and from teacher-reported pupil behaviour questionnaires on 11,571 pupils, both before and after the trial.
The trial ran for a full academic year, though, KiVa is designed to be embedded into ongoing school practice and many schools involved in the trial are continuing to use the programme.
Results
The schools on the KiVa arm of the trial set up fortnightly lessons for pupils which focused on recognising and responding to bullying and helping to support victims. There were also whole-school assemblies on bullying, poster campaigns and information for parents.
For every identified bullying incident, staff followed KiVa’s recommended actions – Rather than the traditional response of blame and punishment for the bully, the schools had individual discussions with the children involved and made sure that the bullying pupil committed to clear actions to support the victim.
The project was led overall by Bangor University working with the Universities of Exeter, Oxford, Warwick, and Birmingham and the trial itself was managed by the Centre for Trials Research, Cardiff University, with the Children’s Early Intervention Trust charity, that has the UK KiVa dissemination licence, organising intervention costs, training schools and implementation.
Circumstances
The results from the UK trial of 13% reduction in bullying are less compelling than those from earlier studies in other European countries. However, the UK trial took place during the Covid-19 pandemic, which involved major classroom disruption for pupils and considerably higher levels of absenteeism, and researchers believe this may have affected the results.
Lucy Bowes, Professor of Psychopathology at the University of Oxford, said: “Being bullied may have devastating consequences for children and young people, including increasing the risk of mental health difficulties such as anxiety or depression, as well as poor school outcomes.
“This means that any improvement is worthwhile and even small percentage changes can have a substantial impact for those individual children and will cumulatively improve the situation in the school over time.
“The Finnish data show year-on-year improvements over seven years for schools that continue with the programme. Addressing bullying in schools is a major public health concern, and evaluating anti-bullying programmes used in our schools is vital.”
‘The effects and costs of an anti-bullying programme (KiVa) in UK primary schools: a multicentre cluster randomised controlled trial’ is published in Psychological Medicine.
Support our Nation today
For the price of a cup of coffee a month you can help us create an independent, not-for-profit, national news service for the people of Wales, by the people of Wales.





I remain worried that too much supposed ‘bullying’ is only young children learning how to interact with others and is a normal part of growth. Children need a few bumps in the way so they can cope with teenaged and adult life – otherwise we end up with all the next generation not being able to work due to ‘nerves’ if we wrap them up in too much woke cotton wool.
Real bullying – by say adolescents – is a differnt kettle of fish.
This sounds good. Bullying is nasty, insidious, evil and demeans many people. It makes them afraid and self harm all the way up to suicide. If this can be nipped in the bud now hopefully this will lead to better people in later life and reduce work place bullying. Again leading to a better quality of life for many people. Break the cycle young, benefits all around.